From 1960 to 2000, there were only 400,000 connected lines in Nigeria (mobile and landlines). The new millennium brought about the arrival of GSM phones and the mass adoption of mobile phones by Nigerians, catapulting the number of connected lines under a decade to 90 million subscribers. This number has risen to over 150 million active subscribers since 2011, and Nigeria currently consumes 29% of Africa’s internet.
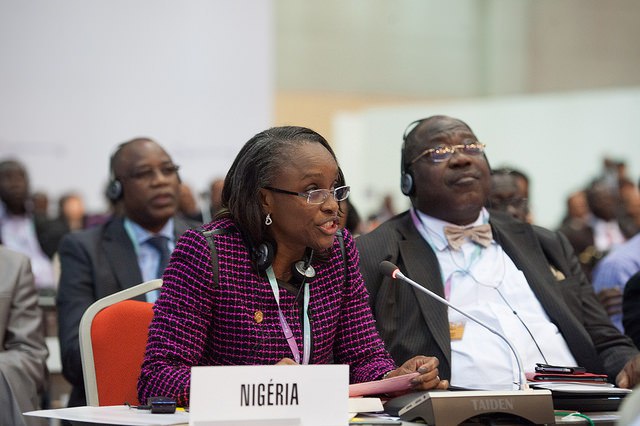
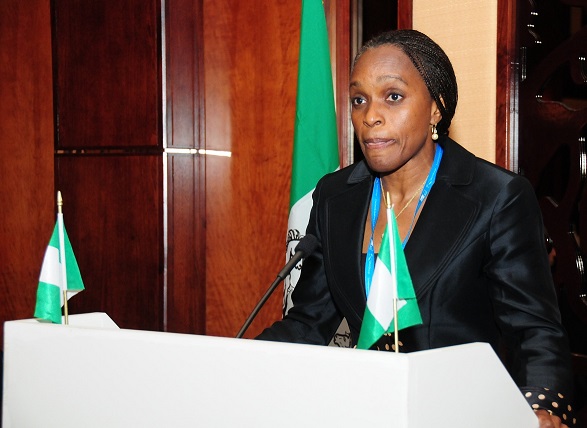
The rapid adoption of ICT around the world and the call for increased sovereign regulation by stakeholders in Nigeria’s ICT industry led to the creation of the Federal ministry of Communications Technology by former president, Goodluck Jonathan. Dr. (Mrs.) Omobola Olubusola Johnson was approved by the senate as the first minister of the new ministry.
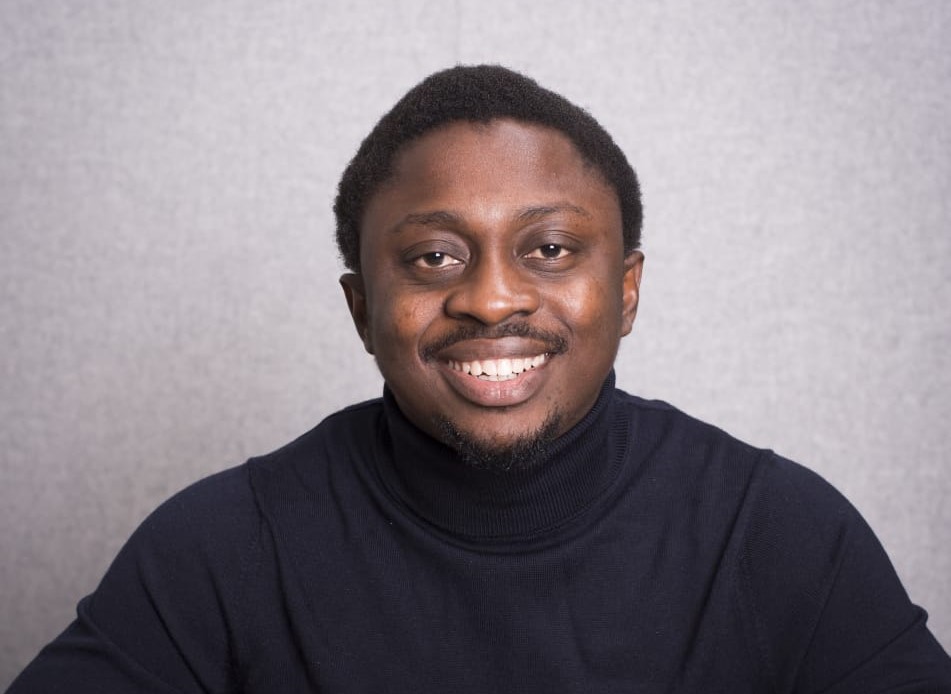
Dr. Johnson
Formally remarked for describing herself as a technocrat rather than a politician, Mrs. Johnson holds a Bachelor's Degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from the University of Manchester; a Masters degree in Digital Electronics from King's College, London; and a PhD from Cranfield University.
She joined Accenture in 1985 and rose to become the Country Managing Director of Accenture in December 2005. She serves as the founding Chairperson and member of Board of Trustees of Women in Management and Business, among others. She served as an Independent Director of Diamond Bank Plc since August 2010 to July 14, 2011. She served as Director of Custodian And Allied Insurance Plc until July 2011. She also currently serves as General Partner at VC firm, TLcom Capital and is also the Honourary Chairperson of the Alliance for Affordable Internet.
Getting to Work
Shortly after her appointment, Johnson was determined to achieve results, a situation that propelled her into putting in motion specific policies and legislation relating to the development of the ICT sector including, National ICT Policy of August 2012; National Broadband Plan 2013-2018 of May 2013; and Guidelines for Nigerian Content in ICT of November 2013. She established a number of initiatives in line with the ministry’s mandate in order to fast track the development of the Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector. Her office set-out to facilitate the build-out of a robust, and cost-effective broadband network aimed at increasing internet penetration within the country.

Be the smartest in the room
Give it a try, you can unsubscribe anytime. Privacy Policy.
These guidelines were submitted in 2013 to the then president, Goodluck Jonathan, to facilitate the accelerated rollout of broadband infrastructures that includes a connected national backbone, regional rings, metro rings and fibre optics to increase broadband penetration from 6 percent to about 30 percent by 2018.
In her bid to ensure quality of service within the telecoms industry, Johnson, within one year, also took proactive steps to tackle the challenges militating against service quality delivery in the country. In collaboration with the Ministry of Works and various state governments, her ministry was able to come up with new ‘Right of Way’ guidelines that ensured good service quality delivery within the industry. Her smart states initiatives significantly reduced Right of Way fees, and standardized state levies and taxes on ICT infrastructure. The ministry also collaborated with the Ministry of Environment to provide guidelines that will address the deployment of base stations required for wireless data and voice transmission.
Her ministry ensured the migration of all governments Ministries, Departments and Agencies (MDAs) to the .gov.ng domain. Her ministry also developed a Government Service Portal and government contact centre to facilitate easy access to government information in an effort to digitize the way the civil service works and to increase transparency and accountability in Nigeria. Johnson was able to set her goals by building her plan around 4 pillars:
Connect Nigeria
This initiative was aimed at speeding up the building out of communications infrastructure so that all Nigerians have access to good quality and affordable, high-speed telecom and internet services.
Through the universal service provision funds, her ministry did a full mapping of the country’s network coverage to establish clusters were it is uneconomical for network providers to operate in. 200 of such clusters were mapped, and about 645,000 people in those clusters have been provided with internet connectivity.
With the USP funds in co-operation with the state governments, the network infrastructure was subsidized to make these clusters, mostly in the rural areas, economic viable for the Telcos to begin operations there, providing voice and internet connectivity.
Through NCC, her ministry was able to supervise the licensing of Infrastructure Companies, InfraCos, to provide efficient wholesale bandwidth services on a non-discriminatory, open access and price regulated basis as well as provide metropolitan fibre and transmission services. It also facilitated increased investment in ICT infrastructure with the licensing of 2.3 Ghz spectrum in March 2014 and another 2.6Ghz auction by first quarter of 2015.
Johnson planned on connecting half of the country’s population to 3G mobile broadband services in 2015. The government is aiming to complete Phase One of a wireless broadband infrastructure upgrade and expansion project, which is part of the National Broadband Plan (2013-2018), by year-end.
Connect Nigerians
This ensures that Nigerians have affordable and convenient access to internet enabled devices and have the capacity to use them; so that all could share in the benefits of ICTs. To ensure the ministry’s vision of Nigeria being the center of innovation and the ICT hub for Africa, different initiatives were set up to connect Nigeria, such as:
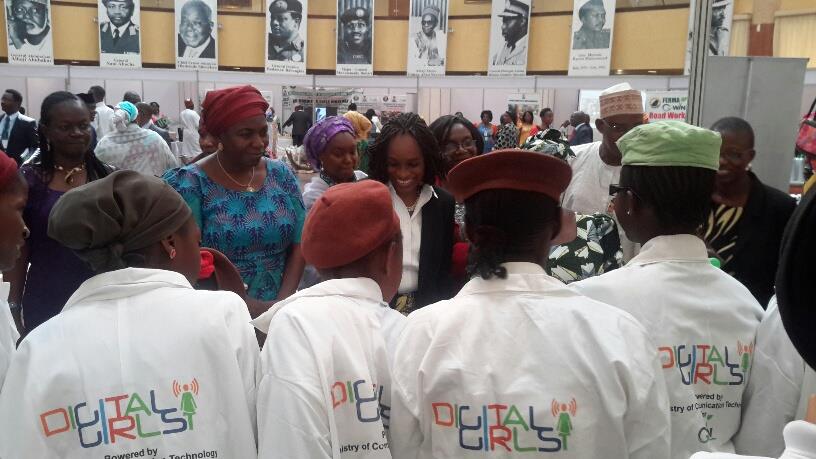
- The Digital Girls Clubs and the 1000 ICT Girls training program are designed to empower Nigerian girls and young women with ICT knowledge. The Digital Girls Club is specifically designed to help Nigerian secondary school girls develop an early interest in computers and information communication technology field as a whole while the goal of the 1000 Girls ICT training program of the Ministry is to build the skills set of Nigerian girls so that they can occupy vacant IT jobs in the country.
- The ministry set up two ICT Incubation Centres- iDEA (Information Technology Developers Entrepreneurship Accelerator) - one in Lagos and the other in Calabar to enhance and grow the ideas and innovations of Nigerian youths into viable globally recognized businesses. iDEA has since opened offices in other parts of Nigeria, their most recent office being based in Ibadan.
- Job and wealth creation training workshop forum tagged Naijacloud exposing youths to the job creation opportunities that people with low to high ICT skills can leverage on via Microworks and eLancing platforms.
Local Content
"The ultimate aim of our policy in this area is to create 'Companies; not code.' Lower entry barriers and significantly increase the size of young local companies in the sector as well as facilitate their sustainability."
Local Content in the industry is targeted at lowering the barriers to entry and increasing the participation of indigenous companies in the ICT sector and stimulating job creation in the industry.
The idea behind building affordable and economic viable ICT infrastructure, is a general economic principle: if you build it, growth will come. This has been stated in a World bank statement the honourable minister is famous for quoting,
"For every 10% increase in bandwidth, there’s a commensurate 1.38% increase in GDP."
With the ICT sector contributing to a tenth of Nigeria’s GDP, the economic benefits of ICT adoption cannot be underappreciated; and this has been corroborated by the rise of many eCommerce companies, notably Jumia and Konga. With Konga starting about two years ago with only 10 staff, and now number over 500 in staffs; of which 100 are engineers developing software. According to the minister, Nigeria's eCommerce sector is now valued at over $550 million.
Facilitating the growth of indigenous companies that will create relevant local content and software for our needs in Nigeria is the key step to connecting Nigerians, creating jobs and the key to the economic benefits that can be reaped from a connected Nigeria.
Another notable case amongst individuals developing technology relevant to the technology space in Nigeria is one of the incubatees who graduated from iDEA, Kayode Disu of iSEC. He secured a 10 million dollar VC funding for his innovation honed by his exposure to iDEA.
Increase the adoption of ICTs by government
With an effort to achieve greater transparency, efficiency, and productivity in governance and citizen engagement, Omobola Johnson introduced the government services portal. The objectives includes creating a single point of entry to government information and services, enhancing accountability and improve the delivery and quality of public services through technology-enabled civic engagement and transforming public administration efficiency through use of the portal. The portal contains a location directory of existing government services that are online and working with Ministries of Agriculture, Education, Health, Industry, Trade & Investment and the ministry to automate some of their processes, most notable of which is the registration of companies with the CAC.
Major Highlights
Some of Omobola Johnson's major achievements, as listed by the Ministry’s permanent secretary, Dr. Tunji Olaopa include:
- Pioneer Minister of Communication Technology responsible for setting up the structure of the Ministry.
- Development of a holistic National ICT Policy that seamlessly integrated its telecoms, postal and IT components.
- Involvement of the ICT/Telecoms industry in policy formulation and feedback through annual Stakeholder workshop.
- Establishment and sustenance of National Council on Communication Technology, to ensure inclusiveness of the States in National ICT adoption and developmental efforts.
- Reinvigorating of a rather challenged NIPOST to make it more relevant in an IT age and more viable through the financial inclusion partnership with CBN to drive cashless policy.
- Implementation of the National ICT Infrastructure Backbone (NICTIB) through the $US100m China EXIM bank loan.
- Initiation and implementation of a ‘Whole-of-Government’ approach in ICT/e-Government – this received a UN Public Service award in 2013.
- Developing and obtaining presidential approval for a National Broadband Plan (2013-2018).
- Development of a National e-Government Master Plan.
- Standardization of the websites of Federal Government Ministries and agencies.
- Adoption of the ‘.gov.ng’ domain name across Federal and state governments.
- Creation and adoption of “@fedcs.gov.ng” email address system for all Civil Servants.
- Creation of the Council of Heads of ICT of Federal Government MDAs to engender unity of purpose in implementation of ICT budgets within the FGN.
- Improved penetration of Telecommunications and Internet services to rural and underserved areas through the targeted focus of the implementation of the USPF.
- Adoption of an Agreed User Policy (AUP) and global Service Level Agreement (SLA) for the shared ICT services by Galaxy Backbone.
- Implementation of various E-Government projects such as – Government Services Portal (GSP), Government Contact Centre (GCC) etc.
- Digitization of the Federal Executive Council (FEC) memo
- Initiation of the Girls’ in ICT program consisting of the – “Digital Girls’ Club”; “1,000 Girls Training” and “Smart Women Initiative” – this program received International recognition by receiving an award at the ITU plenipotentiary in 2014.
- Micro works training – Online Jobs Initiative in collaboration with Rockefeller Foundation (grant of US$ 650,000).
The Communications Technology Ministry portfolio has not been carried over by President Buhari's administration.